Quick Overview
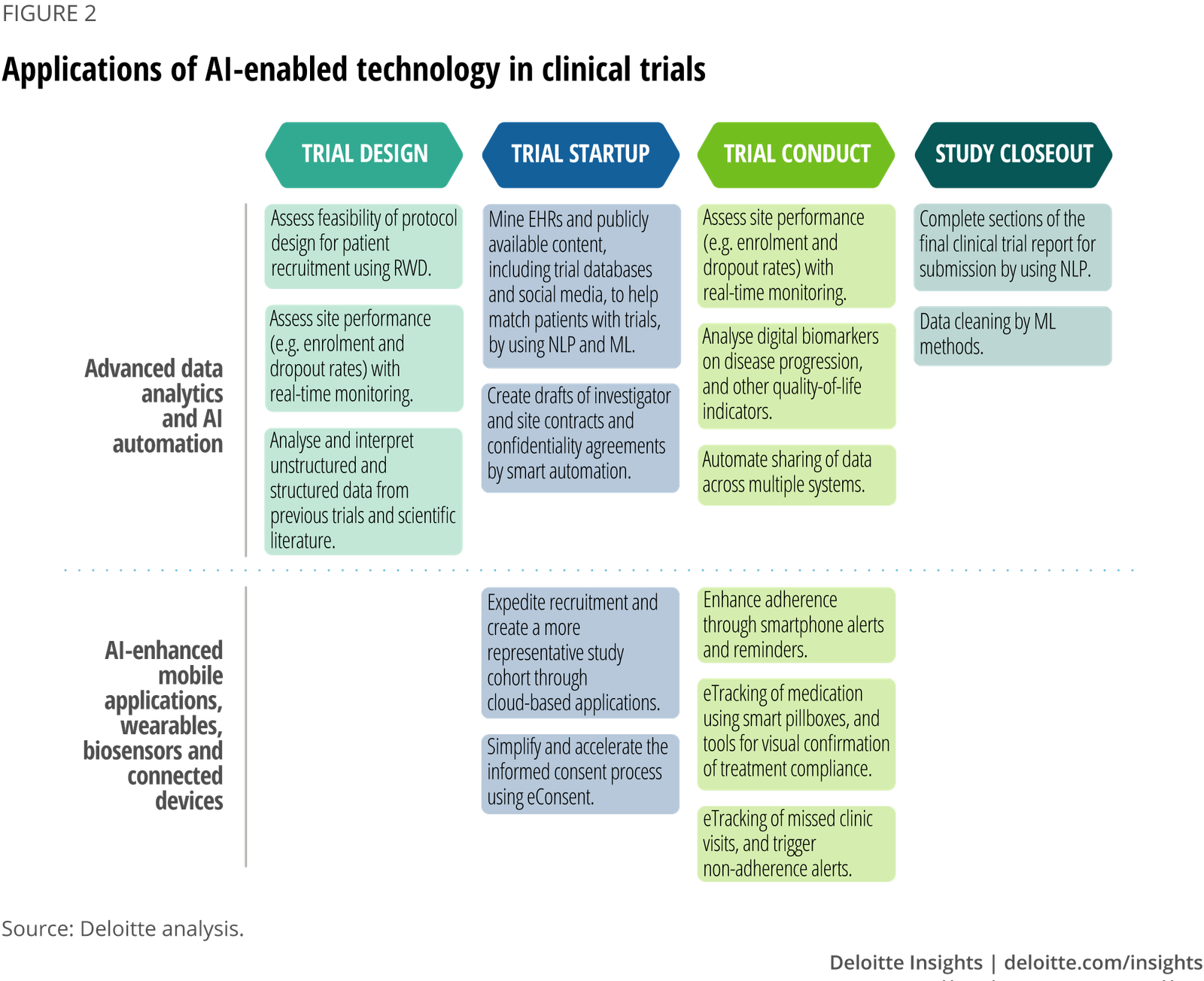
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have created an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm designed to improve the efficiency of matching potential volunteers with suitable clinical trials listed on ClinicalTrials.gov. The study, published in Nature Communications, highlights the capabilities of the algorithm named TrialGPT, which can identify eligible clinical trials and provide clear summaries of how individuals meet enrollment criteria.
Key Features and Advantages
- Efficient Matching: TrialGPT processes patient summaries containing medical and demographic information to find relevant clinical trials.
- Clear Explanations: The algorithm not only identifies eligible trials but also explains how the patient meets the criteria for each study.
- Time-Saving: Clinicians can use the annotated list of trials to discuss options with patients, potentially speeding up the enrollment process.
Study Findings
- The researchers compared TrialGPT’s predictions with assessments made by three human clinicians on over 1,000 patient-criterion pairs, finding that the AI achieved nearly the same accuracy.
- A pilot study showed that clinicians using TrialGPT spent 40% less time screening patients while maintaining accuracy in matching.
Impact on Clinical Research
- Clinical trials are crucial for medical advancements, but finding suitable trials can be a lengthy process.
- TrialGPT aims to streamline this process, allowing clinicians to focus on more complex tasks that require human expertise.
Future Directions
- The research team has received The Director’s Challenge Innovation Award to further evaluate TrialGPT’s performance and fairness in real-world settings.
- There is potential for this tool to enhance clinical trial recruitment and reduce barriers for underrepresented populations in research.
Conclusion
TrialGPT represents a significant advancement in the use of AI for clinical trial matching, promising to improve the efficiency of patient recruitment and support medical research progress.