Research Overview
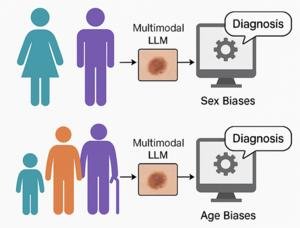
An international research team, led by Assistant Professor Zhiyu Wan from ShanghaiTech University, has published significant findings in the journal Health Data Science. The study reveals biases in multimodal large language models (LLMs), including ChatGPT-4 and LLaVA, when diagnosing skin diseases from medical images. The evaluation focused on various sex and age groups.
Study Details
- The research utilized approximately 10,000 dermatoscopic images.
- It concentrated on three prevalent skin diseases:
- Melanoma
- Melanocytic nevi
- Benign keratosis-like lesions
- Results indicated that while ChatGPT-4 and LLaVA surpassed many traditional deep learning models, ChatGPT-4 demonstrated greater fairness across demographic groups.
- In contrast, LLaVA showed notable sex-related biases.
Expert Commentary
Dr. Wan stated, “While large language models like ChatGPT-4 and LLaVA show promise in dermatology, it is crucial to address the identified biases, especially concerning sex and age, to ensure these technologies are safe and effective for all patients.“
Future Research Directions
The research team plans to conduct further studies that will include additional demographic variables, such as skin tone, to thoroughly assess the fairness and reliability of AI models in clinical settings. This work aims to guide the development of more equitable and trustworthy medical AI systems.
Reference
Wan Z, Guo Y, Bao S, Wang Q, Malin BA. Evaluating Sex and Age Biases in Multimodal Large Language Models for Skin Disease Identification from Dermatoscopic Images. Health Data Sci. 2025 Apr 1;5:0256. doi: 10.34133/hds.0256