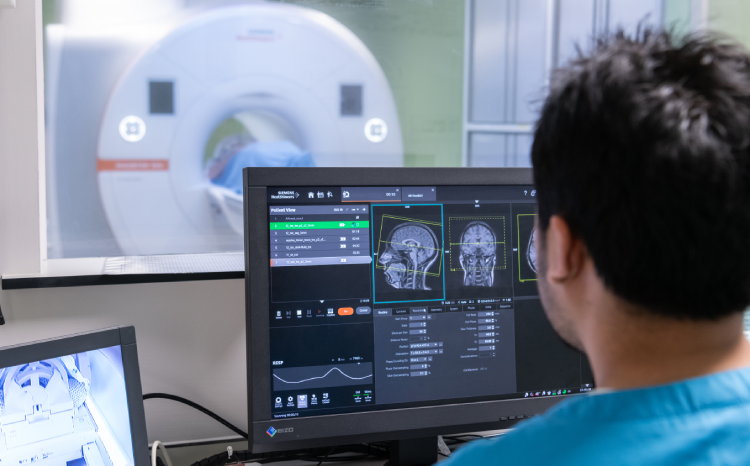
Overview of the Pilot
A recent pilot program at Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust has demonstrated significant improvements in patient care by implementing remote MRI scanning. This initiative, conducted in collaboration with Royal Philips, ran from January 2025 to July 2025 and aimed to explore the feasibility of out-of-hours MRI scanning.
Key Features of the Pilot
- The pilot utilized the Philips Radiology Operations Command Centre technology, allowing radiographers to assist on-site teams from a remote location.
- Scanning appointments were scheduled between 8 PM and midnight, providing patients with greater flexibility.
Impact on Patient Care
By the conclusion of the pilot, the service at one of the trust’s Community Diagnostic Centres was extended from 12 to 16 hours per day, five days a week. This change resulted in:
- 1,356 additional patients being seen during evening hours.
- A reduction in Did Not Attend (DNA) rates from the typical 5-7% to just 1.1%.
- Improved waiting list times for MRI scans.
Patient Feedback
A survey conducted prior to the pilot involving 102 patients revealed that 88% were open to attending appointments outside of traditional hours, indicating a strong demand for flexible scheduling.
Expert Insights
Mark Leftwich, managing director at Philips UK and Ireland, highlighted the ongoing shortage of diagnostic radiographers in England, which contributes to hospital bottlenecks and longer wait times for diagnoses. He stated:
“The possibility of radiographers being able to support on-site colleagues remotely, as well as through extended hours, could truly change the game.”
Training and Workforce Development
The pilot also focused on enhancing the training of radiology staff. Philip Gregory, clinical director at Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, noted:
“Thanks to the Radiology Operations Command Centre, we’ve roughly doubled the number of radiology staff that we can train.”
This innovative approach has allowed for faster and more efficient training, reducing the time required to train radiographers from 20 weeks to just 10 weeks.
Conclusion
The pilot at Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust showcases the potential of remote MRI scanning to improve patient care, reduce waiting times, and enhance staff training. As the NHS continues to face challenges, such initiatives may play a crucial role in delivering better healthcare services.