⚡ Quick Summary
This comprehensive review highlights the recent advancements in three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction technology in thoracic surgery, particularly for lung cancer procedures. The integration of 3D reconstruction significantly enhances surgical accuracy and patient outcomes by improving tumor localization and visualization of critical anatomical structures.
🔍 Key Details
- 📊 Focus: Thoracic surgery, specifically lung cancer surgery
- 🧩 Technology: Three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction
- ⚙️ Applications: Preoperative planning, intraoperative navigation, real-time localization, vascular and airway visualization, postoperative assessment
- 🏆 Innovations: Integration of artificial intelligence to streamline the reconstruction process
- 🚧 Challenges: Image quality limitations, algorithm robustness, and lack of high-quality clinical evidence
🔑 Key Takeaways
- 📈 Increased detection rates of early-stage lung cancers due to chest CT screening.
- 🔍 Transition from traditional lobectomy to parenchymal-sparing sublobar resections, such as segmentectomy.
- 🤖 AI innovations have reduced operative times and increased accuracy in 3D reconstruction.
- 🌟 Enhanced surgical outcomes and patient prognosis through improved anatomical precision.
- 🔮 Future potential for integration with virtual reality and augmented reality technologies.
- 📉 Need for further research to address challenges and validate clinical applications.
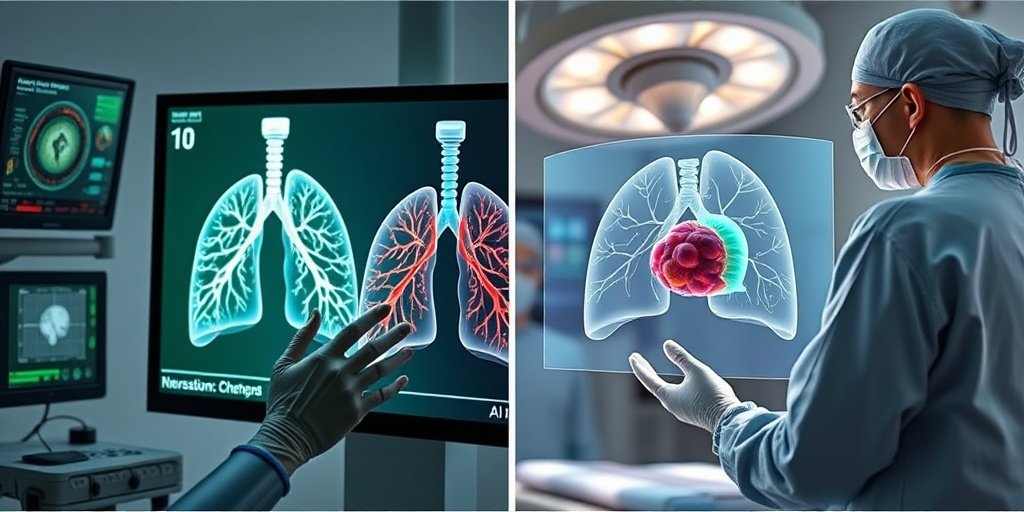
📚 Background
The field of thoracic surgery has seen significant advancements in recent years, particularly with the rise of chest computed tomography (CT) screening. This technology has led to earlier detection of lung cancers, which is crucial for improving patient outcomes. As surgical techniques evolve, there is a growing need for enhanced precision in procedures, especially when transitioning to less invasive options like segmentectomy.
🗒️ Study
This review systematically evaluates the clinical applications of 3D reconstruction technology in thoracic surgery. It emphasizes its role in preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation, which are vital for successful surgical interventions. The authors also discuss the integration of artificial intelligence, which has the potential to automate and enhance the reconstruction process.
📈 Results
The findings indicate that 3D reconstruction technology significantly improves tumor localization and the visualization of vascular and bronchial structures. This advancement contributes to enhanced surgical accuracy and safety, ultimately leading to better surgical outcomes and patient prognosis. However, the review also highlights ongoing challenges, such as image quality and the need for robust algorithms.
🌍 Impact and Implications
The implications of this review are profound. By adopting 3D reconstruction technology, thoracic surgeons can achieve greater precision in their procedures, which is essential for complex surgeries like those involving lung cancer. The potential integration of emerging technologies such as virtual and augmented reality could further personalize and improve surgical approaches, paving the way for intelligent thoracic surgical procedures.
🔮 Conclusion
This review underscores the transformative potential of 3D reconstruction technology in thoracic surgery. As the field continues to evolve, embracing these advancements will be crucial for enhancing surgical precision and improving patient outcomes. Continued research and development are essential to overcome existing challenges and fully realize the benefits of this technology in clinical practice.
💬 Your comments
What are your thoughts on the advancements in 3D reconstruction technology for thoracic surgery? We would love to hear your insights! 💬 Join the conversation in the comments below or connect with us on social media:
Advances in the Application of Three-Dimensional Reconstruction in Thoracic Surgery: A Comprehensive Review.
Abstract
This review presents a comprehensive overview of recent advancements and clinical applications of three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction technology in thoracic surgery, with a focus on lung cancer surgery. The widespread adoption of chest computed tomography (CT) screening has increased the detection rates of early-stage lung cancers, facilitating a transition from traditional lobectomy to parenchymal-sparing sublobar resections, such as segmentectomy, which demand higher anatomical precision. 3D reconstruction technology significantly improves tumor localization, as well as vascular and bronchial visualization, thereby enhancing surgical accuracy and safety. Its key applications encompass preoperative planning, intraoperative navigation, real-time localization, vascular and airway visualization, and postoperative pulmonary function assessment, collectively contributing to improved surgical outcomes and patient prognosis. Recent innovations in artificial intelligence have streamlined and automated the reconstruction process, leading to reduced operative times and increased accuracy. However, challenges persist, including image quality limitations, algorithm robustness, and limited high-quality clinical evidence. Future integration with emerging technologies such as virtual reality and augmented reality holds promise for achieving personalized, intelligent thoracic surgical procedures. This review aims to systematically evaluate the clinical value of 3D reconstruction technology and explore its future development directions.
Author: [‘Lin G’, ‘Li R’, ‘Li X’, ‘Wang D’, ‘Chen X’]
Journal: Thorac Cancer
Citation: Lin G, et al. Advances in the Application of Three-Dimensional Reconstruction in Thoracic Surgery: A Comprehensive Review. Advances in the Application of Three-Dimensional Reconstruction in Thoracic Surgery: A Comprehensive Review. 2025; 16:e70159. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.70159