⚡ Quick Summary
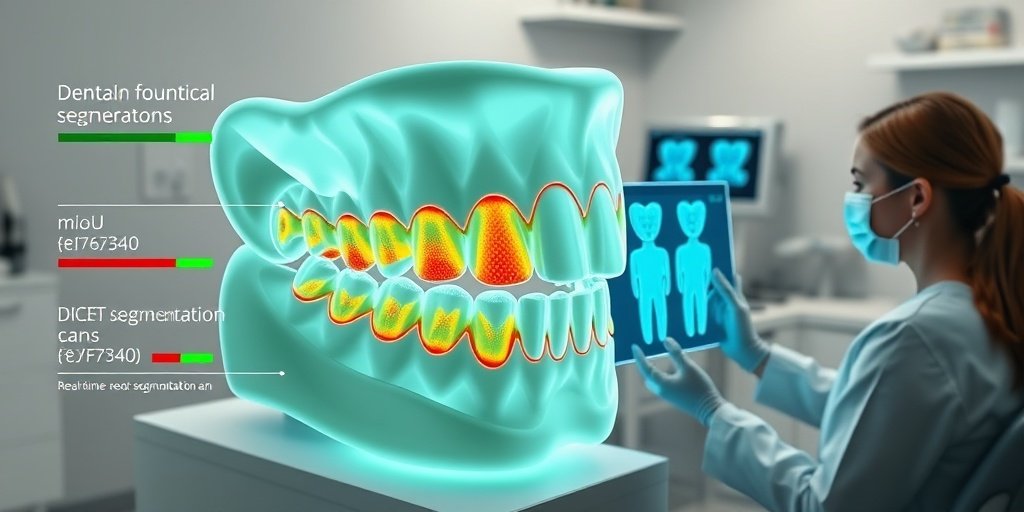
This study presents a novel AI-based multiview segmentation approach for analyzing 3D dental scans, significantly enhancing the accuracy of tooth and gingival boundary identification. The model achieved impressive scores, with a mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) of 93.1% on public datasets and 90.7% on clinical datasets, demonstrating its potential for routine clinical use. 🦷
🔍 Key Details
- 📊 Dataset: 1200 dental models from the 3D Teeth Challenge and 29 clinical 3D intraoral scans
- 🧩 Features used: 3D models converted into multiple 2D images
- ⚙️ Technology: AI segmentation model based on Mask2Former architecture
- 🏆 Performance: mIoU: 93.1% ± 0.09 (public), 90.7% ± 0.01 (clinical); DICE: 95.7% ± 0.09 (public), 94.9% ± 0.01 (clinical)
🔑 Key Takeaways
- 🤖 AI technology can automate the segmentation of dental scans, reducing manual workload.
- 📈 High accuracy achieved with mIoU scores above 90% across different datasets.
- 🌍 Generalizability of the model to real-world clinical scenarios is demonstrated.
- 🦷 Enhanced orthodontic workflows can be supported through this automated approach.
- 💡 Potential for routine clinical use in orthodontics is promising.
- 📚 Study conducted by a team of researchers including Aung ZH and others.
- 🗓️ Published in the Journal of the World Federation of Orthodontists.
📚 Background
The identification of tooth and gingival boundaries in digital models is crucial for effective orthodontic diagnosis, treatment planning, and appliance fabrication. Traditional methods can be labor-intensive and prone to human error. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence offer a promising avenue to automate these processes, enhancing both accuracy and efficiency in orthodontic practices.
🗒️ Study
This study aimed to develop and evaluate an AI-based multiview segmentation approach using a dataset of 1200 dental models and 29 clinical 3D intraoral scans. The researchers employed a modified multiview technique to convert 3D models into multiple 2D images, which were then used to train the AI segmentation model based on the Mask2Former architecture.
📈 Results
The proposed model demonstrated remarkable performance, achieving a mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) score of 93.1% ± 0.09 on the public testing dataset and 90.7% ± 0.01 on the clinical testing set. Additionally, the model recorded a DICE score of 95.7% ± 0.09 for public datasets and 94.9% ± 0.01 for clinical datasets, indicating its robustness and accuracy in segmenting dental structures.
🌍 Impact and Implications
The findings of this study highlight the clinical potential of AI in orthodontics. By automating the segmentation of dental scans, practitioners can expect a significant reduction in manual workload, leading to more efficient workflows. This technology not only enhances the accuracy of digital model analysis but also paves the way for its routine application in clinical settings, ultimately improving patient care and treatment outcomes.
🔮 Conclusion
This research underscores the transformative potential of AI in the field of orthodontics. The development of an accurate and efficient multiview segmentation model for 3D dental scans could revolutionize how orthodontic practices operate, making them more efficient and precise. As we continue to explore the integration of AI in healthcare, the future looks promising for enhanced patient care and streamlined clinical processes.
💬 Your comments
What are your thoughts on the integration of AI in orthodontics? We would love to hear your insights! 💬 Leave your comments below or connect with us on social media:
Towards automated model analysis: A multiview AI segmentation of 3D dental scans.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Precise identification of tooth and gingival boundaries in digital models is essential for effective orthodontic diagnosis, treatment planning, and appliance fabrication. Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) offer opportunities to automate this critical step with accuracy and generalizability. The objective of this study is to develop and evaluate an AI-based multiview segmentation approach that reduces manual workload, and supports daily orthodontic workflows using 3D intraoral scans.
METHODS: A total of 1200 dental models from the public 3D Teeth Challenge dataset and 29 clinical 3D intraoral scans were used. Each 3D model was converted into multiple 2D images using a modified multiview approach. An AI segmentation model, based on the Mask2Former architecture, was trained to segment tooth boundaries automatically. Performance was assessed using mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) and Dice Similarity Coefficient (DICE) scores, comparing results to existing approaches.
RESULTS: The proposed model achieved high accuracy on both public and clinical datasets. On the public testing dataset, it reached an mIoU score of 93.1% ± 0.09 and a DICE score of 95.7% ± 0.09. On the clinical testing set, it maintained strong performance with an mIoU score of 90.7% ± 0.01 and a DICE score of 94.9% ± 0.01, demonstrating its ability to generalize to real-world intraoral scans.
CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrates the clinical potential of our AI-based modified multiview segmentation model for intraoral scans. The approach provides accurate results across varying scan qualities, supporting efficient digital model analysis in orthodontics and promising routine clinical use.
Author: [‘Aung ZH’, ‘Noppadolmongkol S’, ‘Suwunnapang N’, ‘Chaweewannakorn C’, ‘Satravaha Y’, ‘Peanchitlertkajorn S’, ‘Boonpratham S’]
Journal: J World Fed Orthod
Citation: Aung ZH, et al. Towards automated model analysis: A multiview AI segmentation of 3D dental scans. Towards automated model analysis: A multiview AI segmentation of 3D dental scans. 2026; (unknown volume):(unknown pages). doi: 10.1016/j.ejwf.2025.12.002