Quick Summary
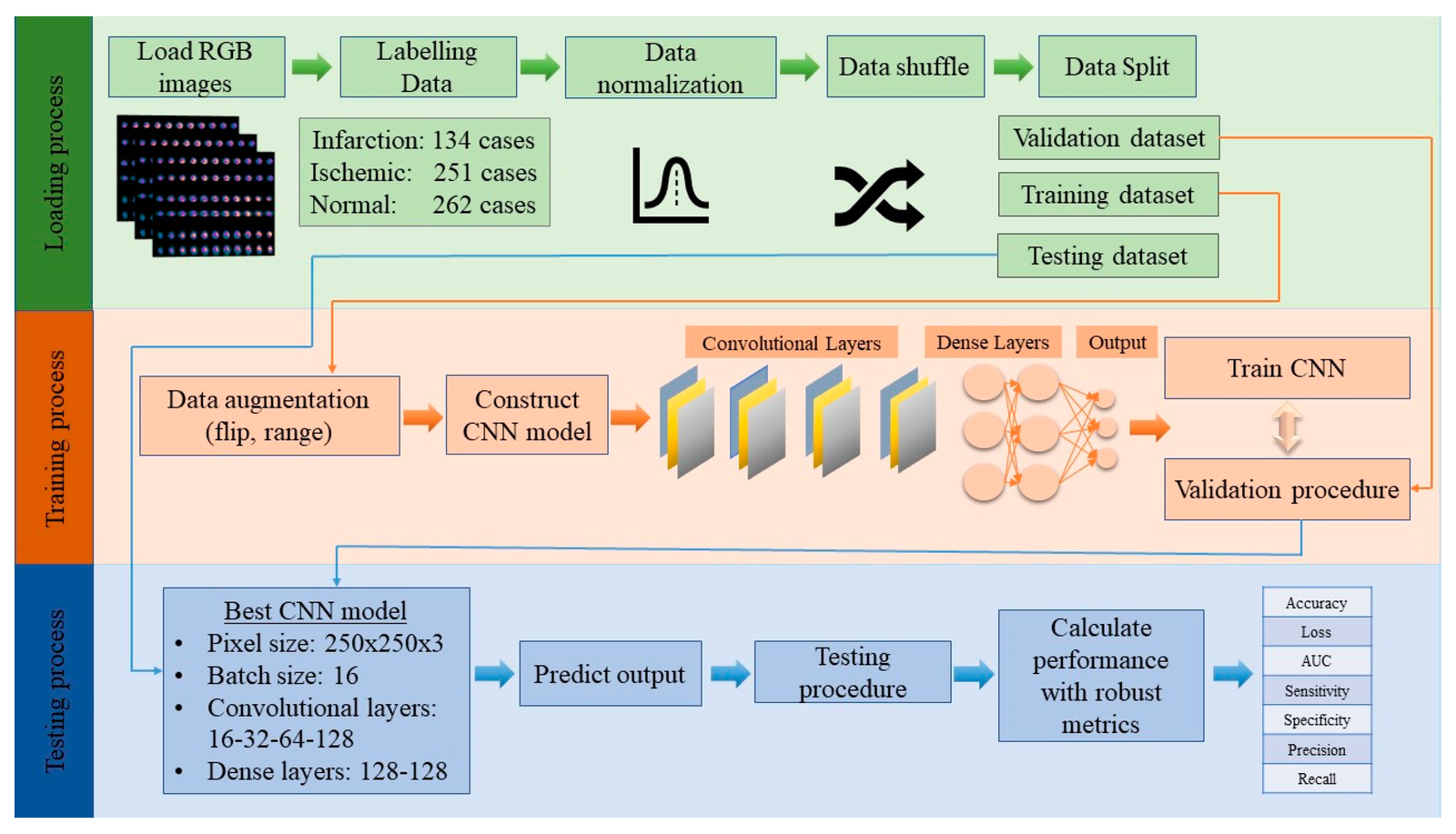
Researchers from Washington University in St. Louis, in collaboration with Cleveland Clinic and the University of California Santa Barbara, have developed a deep learning technique aimed at improving the accessibility and safety of heart imaging. This innovative method, called CTLESS, eliminates the need for additional CT scans in myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI), which is crucial for diagnosing heart disease.
Key Features and Benefits
- Reduced Radiation Exposure: CTLESS removes the requirement for a CT scan, thereby decreasing patient exposure to radiation.
- Cost-Effective: By eliminating the need for an additional scan, this method can significantly lower healthcare costs, especially in resource-limited settings.
- Maintained Diagnostic Accuracy: The deep learning approach ensures that diagnostic accuracy is not compromised, providing reliable heart imaging results.
Research Insights
- The study, led by Abhinav Jha, was published in the IEEE Transactions in Medical Imaging on November 25, 2024.
- CTLESS utilizes photons from the emission scan to create a synthetic attenuation map, enhancing image quality and diagnostic interpretation.
- Initial evaluations using real-world clinical data showed that CTLESS performs comparably to traditional methods across various scanner models and patient demographics.
Future Directions
- The next phase of research will focus on validating the CTLESS method and expanding its availability, particularly in rural hospitals.
- Researchers aim to address the challenges faced by healthcare facilities that lack the necessary equipment for traditional SPECT imaging.
Impact on Healthcare Access
- CTLESS has the potential to improve health equity by making advanced heart imaging more accessible to underserved communities.
- By simplifying the imaging process, it allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient care rather than logistical challenges.
Conclusion
The development of the CTLESS method represents a significant advancement in cardiac imaging technology, promising to enhance patient safety and accessibility while maintaining high diagnostic standards.
Sources
- Multi-input deep learning approach for Cardiovascular Disease diagnosis using Myocardial Perfusion Imaging and clinical data – ScienceDirect
- Deep Learning-Based Automated Diagnosis for Coronary Artery Disease Using SPECT-MPI Images – PMC
- Enhancing the diagnosis of functionally relevant coronary artery disease with machine learning | Nature Communications