Quick Summary
A recent study published in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging reveals that a deep learning model can effectively diagnose and stage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) using just one inhalation lung CT scan. This advancement could simplify the diagnostic process for patients and healthcare providers.
Key Insights
- COPD Overview: COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by breathing difficulties, fatigue, and is the third leading cause of death globally, according to the World Health Organization.
- Traditional Diagnosis: Typically, COPD is diagnosed through spirometry tests that measure lung function, requiring two CT images: one during inhalation and another during exhalation.
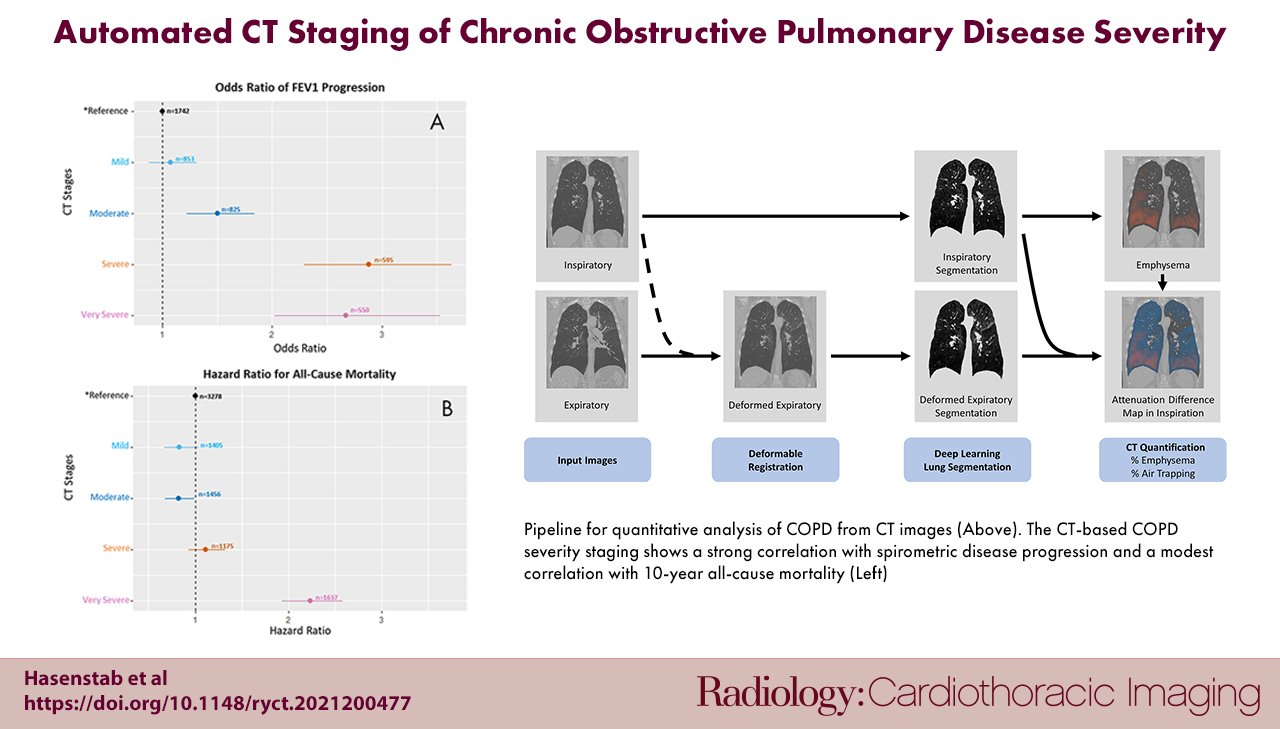
- Study Findings: The study led by Dr. Kyle A. Hasenstab from San Diego State University demonstrated that a convolutional neural network (CNN) could accurately diagnose COPD using only a single inhalation CT image combined with clinical data.
Study Details
- The research analyzed data from 8,893 patients, all with a history of smoking, collected between November 2007 and April 2011.
- The CNN was trained to predict spirometry measurements and subsequently used to determine the Global Initiative for Obstruct Lung Disease (GOLD) stage, which classifies COPD severity.
- Results indicated that the CNN model could diagnose COPD accurately and was consistent within one GOLD stage, comparable to traditional methods requiring two CT scans.
Benefits of the New Approach
- Increased Accessibility: Utilizing a single inspiratory CT scan can make COPD diagnosis more accessible, particularly in institutions lacking the resources for dual imaging protocols.
- Reduced Patient Burden: This method minimizes patient discomfort and exposure to ionizing radiation, while also potentially lowering healthcare costs.
- Improved Accuracy: Incorporating clinical data alongside the CT scan enhances the model’s predictive accuracy.
Future Implications
This innovative approach could lead to more efficient COPD diagnosis and management, ultimately improving patient outcomes and healthcare delivery.
Source
- Lee AN, Hsiao A, Hasenstab KA. Evaluating the Cumulative Benefit of Inspiratory CT, Expiratory CT, and Clinical Data for COPD Diagnosis and Staging through Deep Learning. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2024 Dec;6(6):e240005. doi: 10.1148/ryct.240005